Wialon Hosting
Cloud-based version of Wialon, the ultimate solution for fleet digitalization, designed to streamline operations and enhance efficiency for various fleets — from cars and trucks to heavy vehicles and machinery.
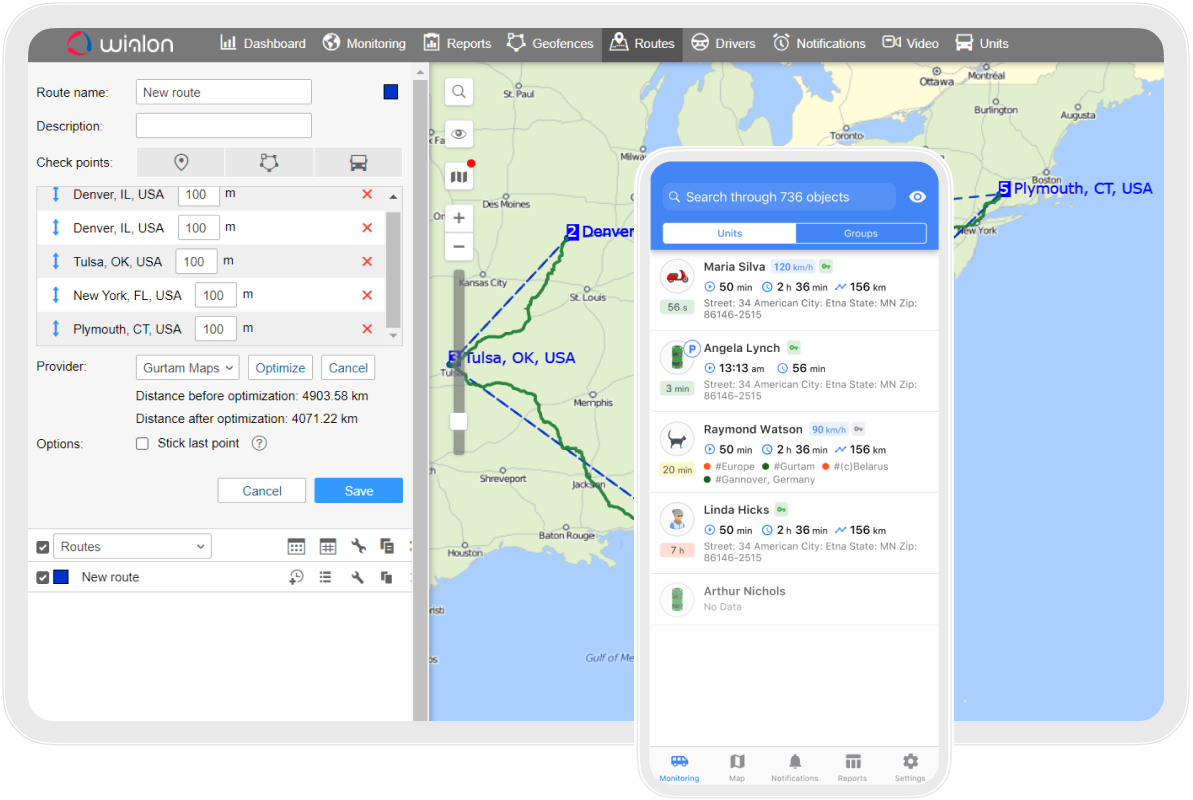
Cloud-based version of Wialon, the ultimate solution for fleet digitalization, designed to streamline operations and enhance efficiency for various fleets — from cars and trucks to heavy vehicles and machinery.
