Advanced properties
To work with the Advanced tab, the user should have full access to the unit.
The Advanced tab consists of several sections. In these sections, you can configure parameters for reports, track and sensor colours, filtering of unit messages, etc.
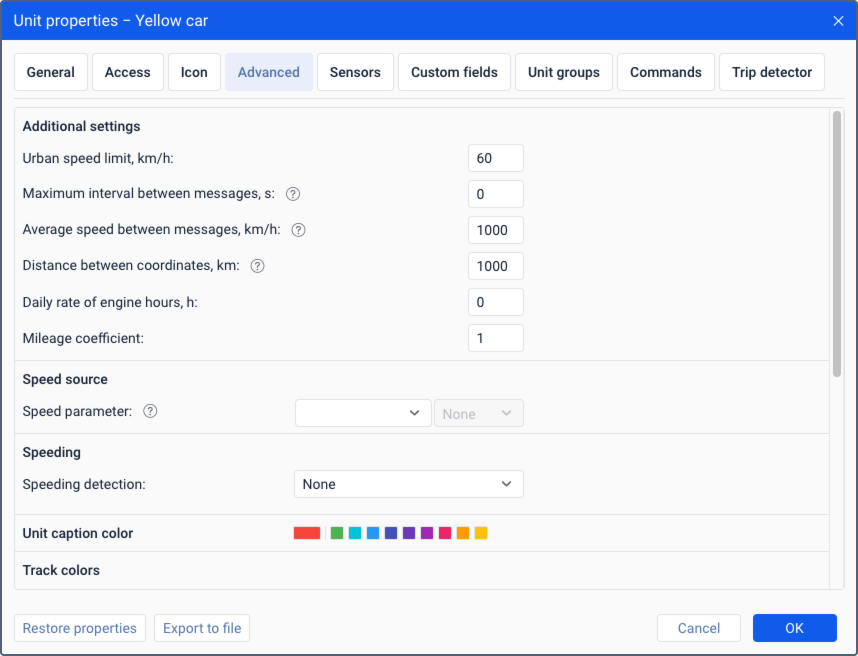
Additional settings
The parameters available in this section influence the calculations of mileage, engine hours and other data.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Urban speed limit | The maximum speed at which it is conventionally considered that the unit is moving within the city. Moving at a higher speed is considered as suburban mileage. |
| Maximum interval between messages | The maximum interval between messages in seconds. If the specified value is exceeded, the system considers it as connection loss. |
| Average speed between messages | This option is used to exclude coordinate outliers when calculating mileage. Maximum average speed of the unit determined by two successive messages, in km/h. If the specified value is exceeded, these messages are not taken into account when calculating the mileage in reports and in the GPS and GPS + engine ignition sensor mileage counter. To disable the option, specify 0. |
| Distance between coordinates | This option is used to exclude coordinate outliers when calculating mileage. Maximum distance between coordinates in two successive messages, in km. If the specified value is exceeded, these messages are not taken into account when calculating the mileage in reports and in the GPS and GPS + engine ignition sensor mileage counter. To disable the option, specify 0. |
| Daily rate of engine hours | The daily rate of engine hours (in hours). This value can be used in the report on engine hours (when calculating utilization and useful utilization). The operation of engine hours is determined by the engine hours counter. |
| Mileage coefficient | The coefficient used to correct the mileage calculated in the system in cases where it always differs from the actual mileage by a certain number of times. Example. The mileage calculated in the system is 100 km, and the actual mileage (determined by the vehicle equipment) is 120 km. The mileage coefficient that should be specified in this field is 120/100 = 1.2. The result of multiplication by the coefficient is shown in the Mileage (adjusted) column in the Geofences report table. |
Speed source
This section is shown for certain device types for which changing the speed source is supported in the monitoring system.
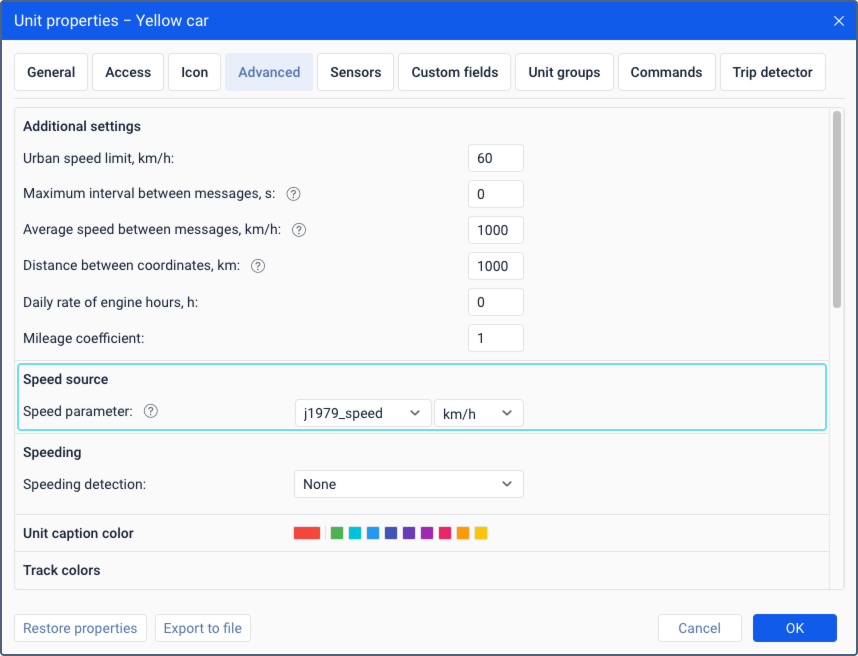
In most cases, the monitoring system uses the values calculated by the device via GPS as speed values. They are stored in the unit messages in the speed parameter. If they are not correct, you can specify the parameter the values of which should be used for the speed parameter.
To set the speed source correctly, follow the steps below.
- In the Speed parameter field, select or specify the name of the parameter (no more than 50 characters) the values of which should be used as speed values. The list shows all the parameters sent by the device, except for the virtual ones.
- Select the unit of measurement in which the device sends speed values (not the unit of measurement which should be shown in the monitoring system). If the unit of measurement is not selected, the system uses km/h.
- Save the changes.
After that, the speed parameter values from the unit messages begin to be replaced by the values of the specified parameter in all parts of the system without the possibility of recovery. If the messages don’t contain the specified parameters, the usual values of the speed parameter are used.
Speeding
In this section, you can select the method which should be used to determine speed limit violations on which you can later run a special report. Also, if you are running a report, you can also enable an option to add speeding markers to the map.
The following items are available for selection:
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| None | The system doesn’t register speed limit violations. This item is selected by default. |
| Fixed limit | Speed limit violations are registered in accordance with the specified conditions. In the Fixed speed limit field, specify the maximum allowed speed for this unit. If the speed is higher than the specified value, the system registers a violation. In the Min. speeding time field, specify how long the violation should last. If the violation lasts less than the specified time, the system doesn’t register it. |
| Road limits | Speed limit violations are registered in accordance with the restrictions for passenger cars indicated in Gurtam Maps (provided that the road limit is higher than 30 km/h). In the Tolerance on speeding field, specify by what value the unit can exceed the speed limit so that the system doesn’t register a violation. For example, the map shows a road limit of 60 km/h. The field value is 10 km/h. This means that if the unit is moving at a speed of up to 70 km/h, no violation is registered. In the Min. speeding time field, specify how long the violation should last in order for the system to register it. If you specify 0 in the Min. speeding time field, a speed limit violation is registered even if the unit sends one message with a speed value higher than the selected limit. The duration of this interval is indicated in reports as 00:00. |
Unit caption colour
By default, the names of the units are shown on the map in red. However, you can select a different colour for each unit.
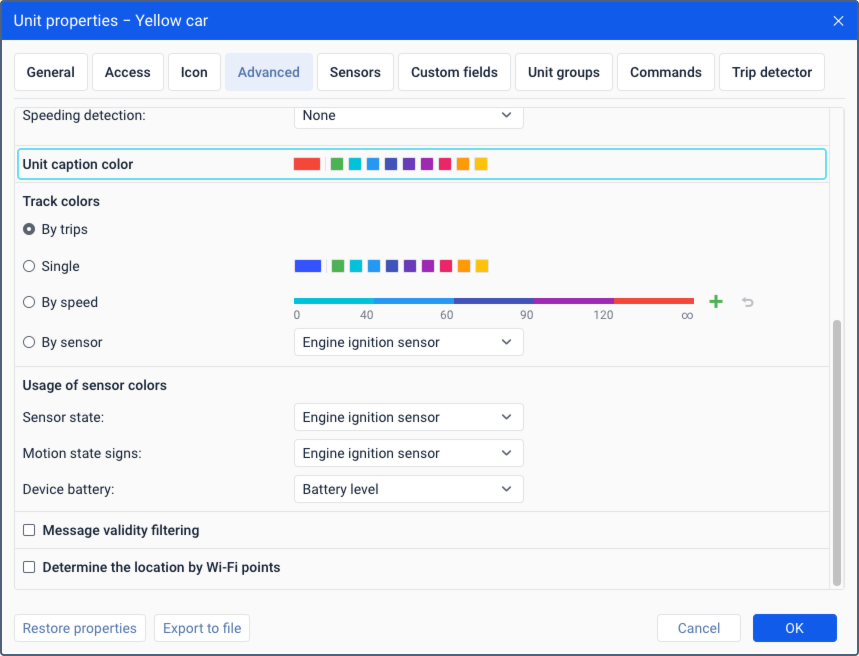
Track colours
In this section, you can set the colour for tracks, that is, the lines of unit movement on the map. The tracks are mapped on the Tracks and Monitoring tabs (the Quick track option).
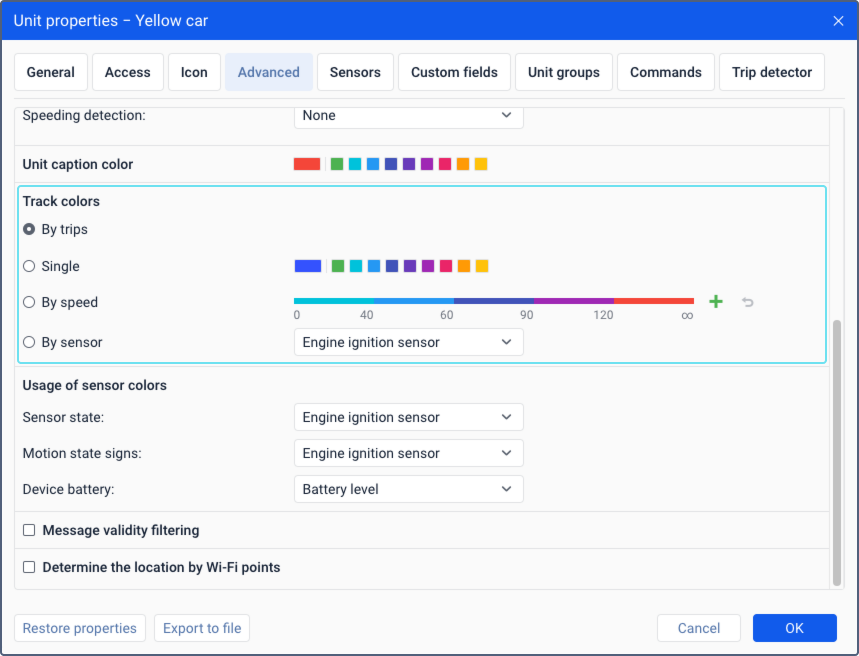
Tracks can be single- or multi-coloured depending on the settings according to which the colour is determined. You can select one of the four options:
- by trips
- single
- by speed
- by sensor
The option selected in this section is also selected for the Tracks tab by default.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| By trips | The track is divided into sections of different colours, each of which corresponds to one trip. Trips are detected by the trip detector. |
| Single | The track is single-coloured. This option is useful when mapping tracks for unit groups because they don’t merge with each other in this way. You can select a colour from the palette. If you map several tracks in a row, the next colour from the palette is used for each track. |
| By speed | The track is multi-coloured depending on the unit speed. To add an interval, click on the icon , specify the speed values and the colour for the interval, and click OK. An empty value in the first field is considered as -∞, in the second as + ∞. You can select the colour from the palette or specify it in the HEX format in the field above. The created intervals are shown on the line scale. To edit an interval, click on it, make changes, and click OK. To reset the settings to the default ones, click on the icon to the right of the scale. |
| By sensor | The track is multi-coloured depending on the values of the selected sensor. The list contains the sensors created for the unit. The value intervals and colours for tracks are specified in the sensor properties.If the interval settings have been deleted from the properties of the selected sensor, the system will automatically switch to another sensor that has the intervals configured. In case there are no other sensors with configured intervals, the system will use the By trips option. |
Usage of sensor colours
In this section, you can select the sensors the colours of which should be used for certain interface elements. The colours are configured in the sensor properties.
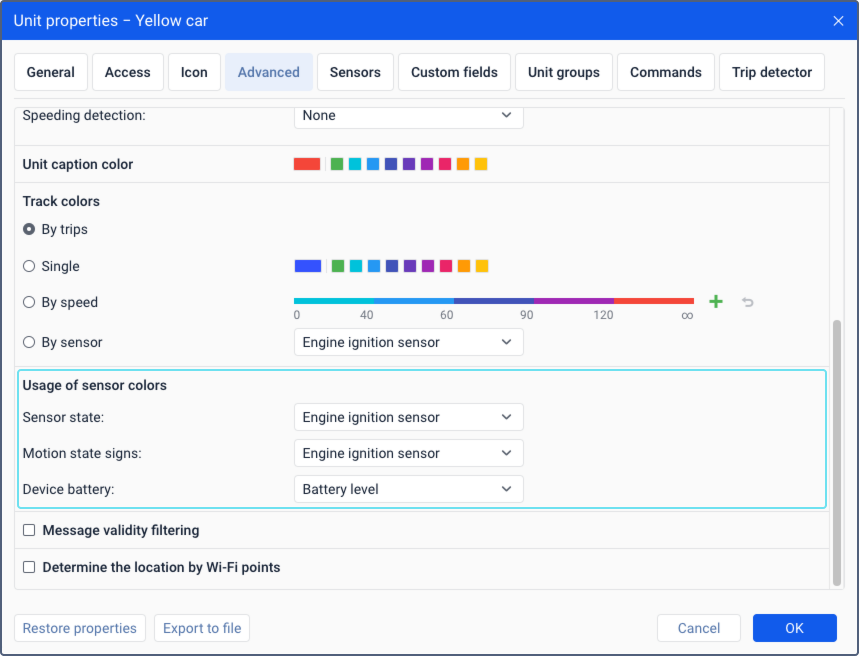
Below are the interface elements for which the colours of the selected sensors are used.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Sensor state | The colours of the selected sensor are used for the Sensor state option in the work list on the Monitoring tab and in the menu of monitoring options on the map. |
| Motion state signs | The colours of the selected sensor are used for motion state signs on the map. |
| Battery level | The colours of the selected sensor are used for the Device battery option in the work list on the Monitoring tab and in the menu of monitoring options on the map.To configure a sensor which shows the battery level, you should create a custom sensor with the parameter in which data on the battery is received from the device. If the data is received in volts, and not in per cent, then you should also fill in the calculation table in the sensor properties so that the data is displayed correctly. |
If the unit doesn’t have suitable sensors, these options are inactive.
Message validity filtering
All messages from units are registered in the database. However, some messages can be invalid, for example, due to data fluctuations or lack of coordinates. Such messages distort the values of mileage, tracks, indicators in reports, etc.
In order for the system not to take invalid messages into account, enable the Message validity filtering option and configure the required criteria: the number of satellites, unit speed, or the accuracy of coordinates. Here you can also enable the options for determining the location by LBS and filtering the messages identified as invalid by the device itself.
Regardless of the settings in this section, any messages with zero or no coordinates are filtered automatically. A message is considered invalid if at least one coordinate (longitude or latitude) is equal to zero.
Filtering is applied only to GPS data, so if an invalid message contains other parameters, for example, sensor values, they can still be used in the system.
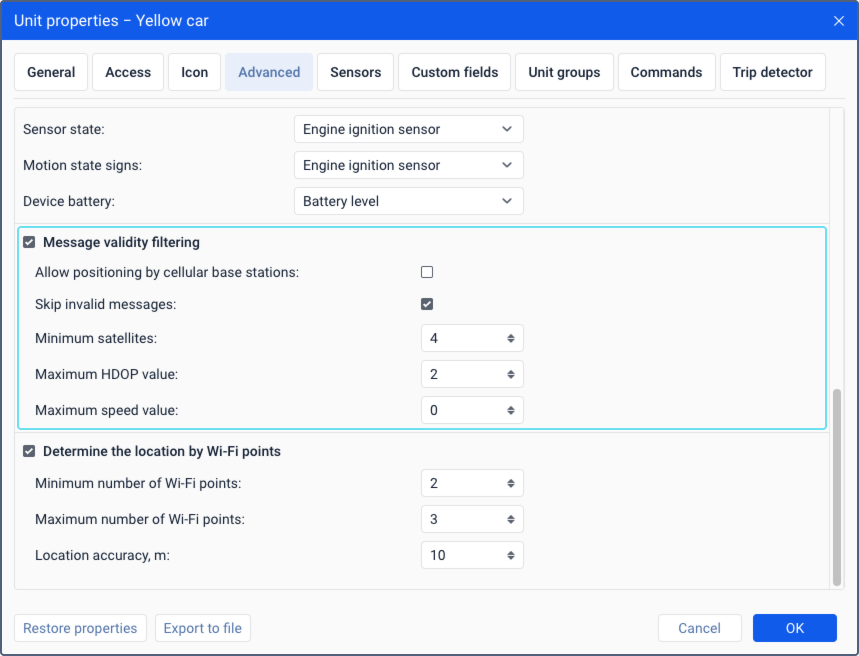
The settings in the section apply only to the messages received after the settings have been adjusted.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Allow positioning by cellular base stations | This option works for devices which support positioning by cellular stations. To see a list of such devices, select the required section on the Hardware tab and apply the LBS filter. The option allows using cellular base stations (LBS) to determine the unit location, for example, when GPS data is not valid. The data obtained this way is not as accurate as GPS data and shows only an approximate location. LBS data is used in the following cases:
During these five minutes, the system shows the unit location and motion state determined by the last valid GPS data. The LBS messages received in the meantime don’t affect the displayed unit location and motion state. After five minutes, if the values of all LBS parameters (mnc, mcc, lac, cell_id) remain the same as in the last message with valid GPS coordinates, these coordinates continue to be regarded as the last known unit location and the motion state icon doesn’t change. As soon as new values of the LBS parameters are received, a new unit location is shown according to them, and the motion state icon changes to . |
| Skip invalid messages | The option allows ignoring the GPS data identified by the device as invalid. Some devices (controllers) send special parameters which identify invalid coordinates. Also, the current time and the last valid coordinates are specified in the message. The system considers such a message to be without positional data and doesn’t use it for mapping tracks, determining the location, and so on. |
| Minimum satellites | In this field, you can specify the minimum number of satellites that should be used to determine the coordinates in order for the message to be considered valid. The recommended number is at least four. The value can’t exceed 255. |
| Maximum HDOP value | In this field, you can specify the maximum HDOP value with which messages are considered valid. HDOP stands for horizontal dilution of precision. The smaller this value is, the more accurate the coordinates are. The value can’t exceed 9,999. |
| Maximum speed value | In this field, you can specify the limit for speed values. If it is exceeded, the message is considered invalid. You can’t indicate a value greater than 9,999. If 0 is specified, this filtering criterion is not taken into account. |
If the speed or HDOP value exceeds the maximum allowed one, or the number of satellites is lower than the specified one, the following data of the message becomes unavailable: speed, coordinates, number of satellites, and altitude.
Determine the location by Wi-Fi points
This option is displayed for devices that can determine the location by Wi-Fi points. To see a list of such devices, select the required section on the Hardware tab and apply the Wi-Fi positioning filter.
When the Determine the location by Wi-Fi points option is activated, the options described below become available.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Minimum number of Wi-Fi points | Here you should specify the minimum number of Wi-Fi points with which the messages should be considered valid. You can indicate only an integer value. The minimum allowed value is 2, the maximum one is 255. |
| Maximum number of Wi-Fi points | In this field, you should specify the maximum number of Wi-Fi points which should be taken into account when determining the unit location. If the number of available points is greater than the number indicated here, the points with a stronger signal are used. You can indicate only an integer value. The minimum allowed value is 2, the maximum one is 255. |
| Location accuracy, m | In this field, you should specify the location accuracy in meters. The smaller the value, the more accurate the received coordinates. A message is considered invalid if its accuracy value is greater than the specified one. You can enter an integer or fractional number more than or equal to zero. The maximum allowed value is 10,000. |
If the Allow positioning by cellular base stations option (see the section above) is also enabled for the unit and there is valid GPS, LBS and Wi-Fi data, the system determines the unit location using Wi-Fi data in the first place. If Wi-Fi data is invalid (that is, doesn’t match the specified settings or the point address hasn’t been found), the system uses GPS data. LBS data is the last to be used.
You can see that the unit location has been determined by Wi-Fi points in the work list of the Monitoring tab (the Motion state option).
