Advanced Properties
On the Advanced tab of the unit properties, you can specify various parameters for generating reports, adjust colors for tracks, and set speed limitations.
The required access rights:
- View detailed properties. To view parameters for reports, driver activity source, and message filtration;
- Edit not mentioned properties. To edit the color schemes of tracks or sensors;
- Edit trip detector and fuel consumption. To edit report parameters and driver activity source;
- Edit connectivity settings. To edit the parameters of message filtration.
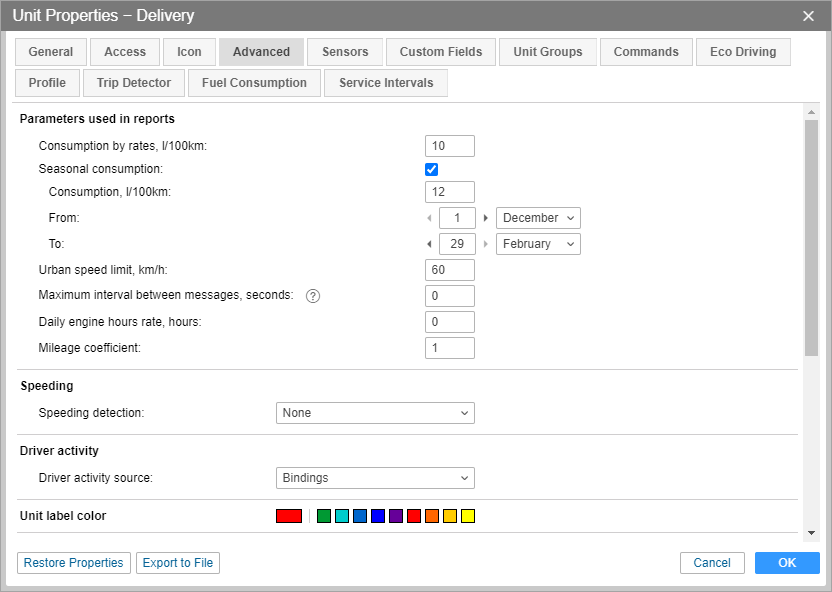
Parameters used in reports
Consumption by rates, l/100 km
In this field, you can indicate the fuel consumption per 100 km. To modify it, you should have the Edit trip detector and fuel consumption access right to the unit. You can indicate positive numerical values here. By default, the value is 0.
Seasonal consumption
Activate this option to set the seasonal calculation of the fuel consumption rate. Specify the fuel consumption per 100 kilometers (default value is 0) and the period (from — to) when this value should be taken into account. To modify this field, you should have the Edit trip detector and fuel consumption access right to the unit.
If the Seasonal consumption option is activated, then when a new sensor is created with the help of the math consumption wizard, the Seasonal multiplier, % option is activated there by default, and the value of the coefficient is counted in accordance with the values specified on the Advanced tab.
Urban speed limit, km/h
Indicate the speed to which it should be considered that the unit is moving in the city. Driving at the speed which is greater than the indicated one is considered a county mileage. You can use this property in the trips reports, statistics, and in the advanced reports on drivers.
Maximum interval between messages
Indicate the maximum interval between messages (in seconds). The excess of the indicated value is interpreted by the system as a connection loss. This is displayed in the report on connection problems, while calculating intervals in the report on engine hours and during the calculation of fuel consumption by mathematical calculation or by FLS.
Daily engine hours rate
Indicate the daily rate of engine hours (in hours). You can use this value in the engine hours report (when calculating the utilization and useful utilization). The engine hours operation is defined by engine hours counter.
Mileage Coefficient
You can use the mileage coefficient to compare the detected mileage with the mileage by odometer. You can include the corresponding columns in any tabular report which contains information about mileage, and in the statistics.
Speeding
In this block, you can select a method for speeding detection can be selected. The selected option defines the order of further actions.
None
By default, the option None is selected. It means that speedings are not registered by the system. This option is useful, for example, for stationary units because it is impossible to determine their speed.
Use fixed limit
For the Use fixed limit method, the maximum speed limit is specified individually for each unit in the Fixed speed limit, km/h field. Upon receiving messages with the speed higher than the indicated one, the system registers a speeding. For this method, you can also enter the minimum speeding duration in seconds (1 second by default) in the Min speeding time, seconds field. The system does not register the speeding the duration of which is shorter than the indicated speeding time.
Use limits from roads
The Use limits from roads method is supported only by Gurtam Maps cartographic service.
With the Use limits from roads option, the speeding registration depends on the speed limitations indicated in Gurtam Maps (provided that the road limit is higher than 30 km/h). In other words, the system contains the data on speed limits for the particular road section, and if a unit exceeds this speed limit while moving by this section, the speeding is registered. When selecting this method, you can indicate the tolerance on speeding value in the Tolerance on speeding, km/h field. In this case, a speeding is considered to be the movement at a speed that is higher than the sum of the values of speed limit and the tolerance on speeding. For example, in some countries exceeding the speed limit by 10 km/h is not a violation, that is why you can indicate 10 km/h tolerance on speeding. Therefore, by a road with the speed limit of 60 km/h, the unit can move with a speed of 70 km/h, and this speed is not considered as speeding. Here you can also indicate the minimum speeding duration in seconds.
If zero (0) is indicated in theMin speeding time, seconds field, the speeding is registered even if there is only one message with speeding, The duration of such interval in the reports is 00:00.
Speedings are registered in the system, and subsequently, you can generate a speeding report. Moreover, during building a track you can enable speeding markers which highlight the corresponding events on the track.
Driver activity
Information on driver activity helps to track whether the driver follows the AETR standards or not. Such information is displayed in the unit or driver tooltips as well as in the extended unit information if the Driver’s activity option is enabled in the user settings.
In this section, you can select a driver activity source. There are three options available in the dropdown list: None, Tachograph, and Bindings. If the None option is selected, the unit or driver tooltips or the extended unit information do not display the current driver activity data. If the Tachograph option is selected, the information on the driver activity bound to this unit is received from the tachograph installed in the vehicle. If the Binding option is selected (for example, if a vehicle is not equipped with a tachograph), the activity of the driver bound to this unit is determined in the following way:
- The Driving status is registered as the driver activity when either trip or stop have been detected for the unit.
- The Work status is registered when parking has been detected.
- The Rest status is registered upon unbinding the driver from the unit.
Unit label color
By default, the names of the units and drivers assigned to the units are displayed in red on the map. You can select different color for every unit.

Track colors
You can set different colors to the unit movements (tracks) on the map.
You can build tracks on the Tracks, Messages, Reports, or Monitoring (the Quick track option) tabs.
Different parts of the track can have different colors. You can set a color in the Track colors section on the Advanced tab in the unit properties. There are 4 mutually exclusive options available: By trips, Single, By speed, By sensor. The option selected in the unit properties is also selected for it in the tracks panel by default.
By trips
The By trips option is designed to change the track color in accordance with the trips which are determined by the trip detector.
Single
This Single option is designed to set one color for the track, which is convenient, for instance when building tracks for unit groups so that they do not visually merge with each other. You can select the track color in the palette.
When you sequentially build several tracks for one unit, a different color is used for each of them (taken in order from the palette).

By speed
If this option is enabled, the track color changes depending on the speed. To set the values for the speed ranges and indicate their colors, click on the Add range icon ( ), choose the track color and click OK. The color for every rage is set individually. You should pay attention to some peculiarities described below.
), choose the track color and click OK. The color for every rage is set individually. You should pay attention to some peculiarities described below.
No value in the first field corresponds to -∞, in the second corresponds to +∞.
When you add an interval that intersects with an existing one and goes beyond its boundaries, the added interval overwrites the existing interval.
When you add an interval that intersects with an existing one and does not exceed its boundaries, a new interval is inserted inside the existing one. Both intervals into which the existing one has been divided receive its color.
You can select a color from the palette or specify it in the HEX format in the field above it.
The created intervals of the selected color are displayed on the scale. To edit the interval, click on it with the left mouse button, make the changes and click OK. To reset the settings to their default state, click on the icon  to the right of the scale.
to the right of the scale.

By sensor
This option is designed to change the color of the track depending on the sensor values. Select a sensor from the dropdown list of the created sensors for the unit). For each created sensor, you can set the interval values and pick their colors. When this option is activated, the colors indicated on the interval scale in the properties of the selected sensor are used to draw the track.

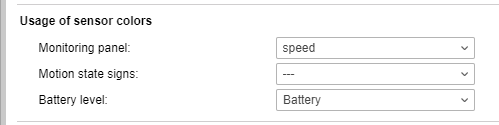
Usage of sensor colors
In this section there are three dropdown lists that allow selecting the sensors the colors of which should be used for:
- displaying the sensor state in the list of units on the Monitoring tab;
- indicating by color the last sensor state of the unit on the map;
- displaying the battery level of the device in the work list on the Monitoring tab and in its monitoring options menu on the map.
If the unit does not have proper sensors, the options are inactive.
To configure a sensor that displays the battery level, you should create a custom sensor with the parameter in which the device sends data about the battery. If the data is in volts insted of percent, you should fill in the calculation table for the sensor in order to display them correctly in the system.
Messages validity filtration
All the messages are stored in the system without any exception. However, in the case of data spikes, lack of coordinates, etc. such messages can distort the mileage count and various indications in the reports. You can enable the filtration in which invalid messages are not taken into account. To do this, enable the Message validity filtration option and fill in the additional fields. The filtration is applied only to new messages.
Allow positioning by cellular base stations
Positioning by cellular base stations (LBS detection) is an alternative method of defining unit location. This method involves the use of cellular base stations as reference points for the location detection. This method is not as accurate as the use of GPS, and allows to determine only the approximate location of the unit. The LBS detection data is used only when the Allow positioning by cellular base stations and Skip invalid messages options are enabled and GPS data is lower than the values indicated in the filtration.
Skip invalid messages
Some devices (controllers) can send special parameters in which the validity or invalidity of coordinates is determined. When preparing a message to be sent to the server, these devices set the current time and the last valid coordinates, and determine the message invalid. Such a message is considered by the system as the message without positional data that is why it is not used when building movement tracks, determining unit position at the time of an event (in reports), etc. However, if this message contains other parameters, for example, sensor values, these parameters are used when building tracks.
Minimum satellites
Here you should indicate the minimum number of satellites with which messages should be considered valid. The recommended value is at least four.
Maximum HDOP value
HDOP (Horizontal Dilution of Precision) is an error in the horizontal plane at which the messages are considered valid. The smaller this parameter, the more accurately the coordinates are determined. If the HDOP value in the message is greater than the specified value, this message is considered invalid. Any messages with missing or zero coordinates are also filtered, even if the device has not determined this message invalid. A message is considered invalid if at least one coordinate (longitude or latitude) is zero.
Maximum speed value
The messages containing speed higher than or equal to the value indicated here are considered invalid. The default 0 value does not affect the filtration.